Configuration API
Cypress enables you to dynamically modify configuration values and environment variables from your plugins file.
Usage
⚠️ This code is part of the
plugins file
and thus executes in the Node environment. You cannot call Cypress or cy
commands in this file, but you do have the direct access to the file system and
the rest of the operating system.
To modify configuration, you return an object from your plugins file exported function.
// cypress/plugins/index.js
module.exports = (on, config) => {
console.log(config) // see everything in here!
// modify config values
config.defaultCommandTimeout = 10000
config.baseUrl = 'https://staging.acme.com'
// modify env var value
config.env.ENVIRONMENT = 'staging'
// IMPORTANT return the updated config object
return config
}
Whenever you return an object from your pluginFile, Cypress will take this and
"diff" it against the original configuration and automatically set the resolved
values to point to what you returned.
If you don't return an object, then configuration will not be modified.
The config object also includes the following extra values that are not part
of the standard configuration. These values are read only and cannot be
modified from the plugins file.
configFile: The absolute path to the config file. By default, this is<projectRoot>/cypress.json, but may be a custom path orfalseif using the--config-fileflag.projectRoot: The absolute path to the root of the project (e.g./Users/me/dev/my-project)
Resolved values will show up in the "Settings" tab of the Test Runner.
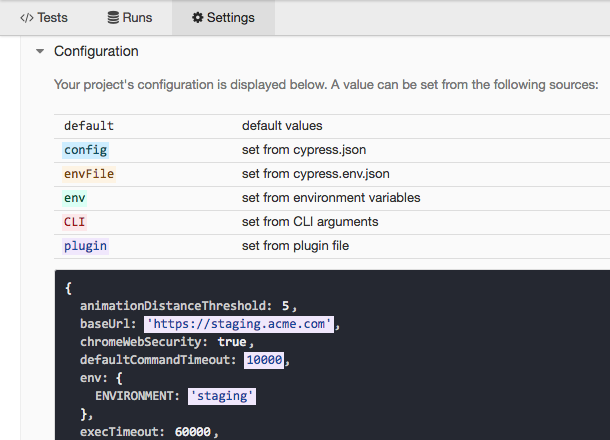
Promises
Additionally, Cypress will respect and await promises you return. This enables you to perform asynchronous tasks and eventually resolve with the modified configuration object. See the example on switching between multiple configuration files for a full example.
Examples
Customize available browsers
The configuration includes the list of browsers found on your system that are available to Cypress.
Read our full guide on Launching Browsers for more information on how this works.
In the plugins file, you can filter the list of browsers passed inside the
config object and return the list of browsers you want available for selection
during cypress open.
// cypress/plugins/index.js
module.exports = (on, config) => {
// inside config.browsers array each object has information like
// {
// name: 'chrome',
// family: 'chromium',
// channel: 'canary',
// displayName: 'Canary',
// version: '80.0.3966.0',
// path:
// '/Applications/Canary.app/Contents/MacOS/Canary',
// majorVersion: 80
// }
return {
browsers: config.browsers.filter((b) => b.family === 'chromium'),
}
}
When you open the Test Runner in a project that uses the above modifications to your plugins file, only the Chrome browsers found on the system will display in the list of available browsers.
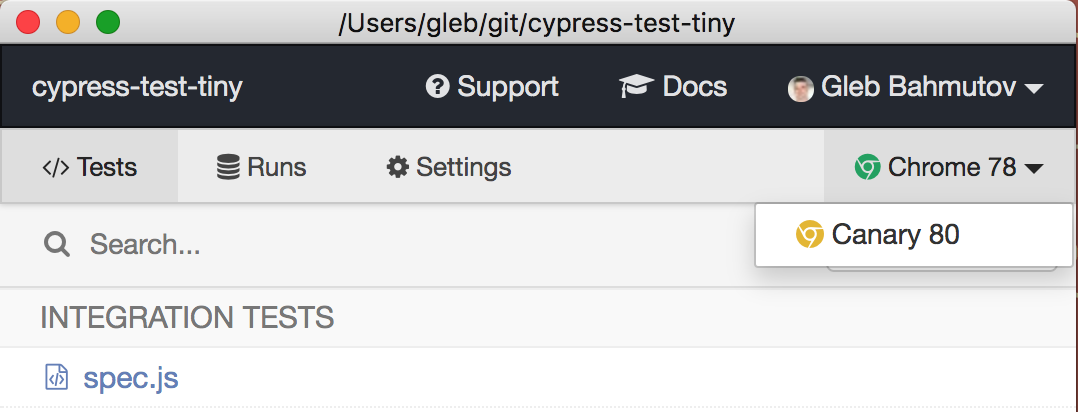
If you return an empty list of browsers or browsers: null, the default list
will be restored automatically.
If you modify the list of browsers, you can see the resolved configuration in the Settings tab of the Test Runner.
Switch between multiple configuration files
This means you can do things like store multiple configuration files and switch between them like:
cypress.qa.jsoncypress.dev.jsoncypress.prod.json
How you choose to organize your configuration and environment variables is up to you.
// promisified fs module
const fs = require('fs-extra')
const path = require('path')
function getConfigurationByFile(file) {
const pathToConfigFile = path.resolve('..', 'config', `${file}.json`)
return fs.readJson(pathToConfigFile)
}
// plugins file
module.exports = (on, config) => {
// accept a configFile value or use development by default
const file = config.env.configFile || 'development'
return getConfigurationByFile(file)
}
You could now swap out configuration + environment variables like so:
cypress run
cypress run --env configFile=qa
cypress run --env configFile=staging
cypress run --env configFile=production
Each of these environments would read in the configuration at these files:
cypress/config/development.json
cypress/config/qa.json
cypress/config/staging.json
cypress/config/production.json
This would enable you to do things like this:
// cypress/config/development.json
{
"baseUrl": "http://localhost:1234",
"env": {
"something": "development"
}
}
// cypress/config/qa.json
{
"baseUrl": "https://qa.acme.com",
"env": {
"something": "qa"
}
}
// cypress/config/staging.json
{
"baseUrl": "https://staging.acme.com",
"env": {
"something": "staging"
}
}
// cypress/config/production.json
{
"baseUrl": "https://production.acme.com",
"env": {
"something": "production"
}
}
This is a less complicated example. Remember - you have the full power of Node at your disposal.
How you choose to edit the configuration is up to you. You don't have to read
off of the file system - you could store them all in memory inside of your
pluginsFile if you wanted.
Runner Specific Plugins
You can access the type of tests running via the config.testingType property.
The testing type is either e2e or component depending on if the E2E or
Component Testing runner was
launched. This allows you to configure runner specific plugins.
Use Cypress React Plugin Conditionally
Conditionally apply the Cypress React Plugin if launching via Component Testing:
module.exports = (on, config) => {
if (config.testingType === 'component') {
require('@cypress/react/plugins/react-scripts')(on, config)
}
return config
}
History
| Version | Changes |
|---|---|
| 7.0.0 | Added testingType property to config. |
See also
- The Configuration section of the Cypress Testing Workshop
- blog post Keep passwords secret in E2E tests